|
ACETYL TRIBUTYL
CITRATE
|
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 77-90-7 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 201-067-0 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Acetylcitric Acid, Tributyl Ester; | |
| 2-acetyltributylcitrate; Acetyl Butyl Citrate; Acetyl Tributyl Citrate; Tributyl 2-(Acetyloxy)-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate; | ||
| 1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic Acid, 2-(Acetyloxy)-, Tributyl Ester; Tributyl Acetylcitrate; Tributyl Citrate Acetate; Tributyl O-acetylcitrate; O-acetilcitrato de tributilo; O-acétylcitrate de tributyle; 2-acetoxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic Acid Tributyl Ester; Tributyl 2-acetoxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate; | ||
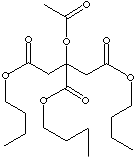
| FORMULA | CH3CO2C[CO2(CH2)3CH3][CH2CO2(CH2)3CH3 | |
| MOL WT. | 402.88 | |
| SMILES | Citric Acid Esterification and acetylation | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Clear viscous liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | -80 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 172 - 174 C at 1 mm Hg | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.05 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble | |
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
||
| pH |
|
|
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| HENRY'S LAW |
|
|
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 0 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | 204 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||
| Acetyl Tributyl Citrate is a plasticizer or carrier solvent permitted in the field of food additive, food contact material as well as for polymers specially for cellulosics. It is also used in synthesis flavoring substances and adjuvants. Acetyl Tributyl Citrate can be used as a component of adhesives. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
Clear viscous liquid | |
|
ASSAY |
99.0% min |
|
| ACIDITY | 0.2 min (mg KOH/gr), (as CITRIC ACID | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.045 - 1.055 | |
|
MOISTURE |
0.3% max |
|
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
|
|
COLOR , APHA |
50 max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 200 kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |
| UN NO. | ||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF CITRIC ACID |
||
|
Citric Acid (2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid, in IUPAC naming) is a
colourless crystalline organic compound belong to carboxylic acid family. It
exists in all plants (especially in lemons and limes) and in many animal tissues
and fluids. In biochemistry, it is involved in important metabolism of almost
all living things; the Krebs cycle (also called citric acid cycle or
tricarboxylic acid cycle), a part of the process by which animals convert food
to energy. Citric acid works as a preservative ( or as an antioxidant) and
cleaning agent in nature. It is commercially obtained by fermentation process of
glucose with the aid of the mold Aspergillus niger and can be obtained
synthetically from acetone or glycerol. It can be used as an sour taste enhancer
in foods and soft drinks. The three carboxy groups lose protons in solution;
resulting in the excellent pH control as a buffer in acidic solutions. It is
used as a flavouring, stabilizing agent and acidulant (to control acidity) in
food industry, in metal-cleaning compositions as it chelates metals. Citric acid
is available in forms of anhydrous primarily and in monohydrate, the
crystallized form from water. The hydrated form will be converted to the
anhydrous form above 74 C. Citrate is a salt or ester of citric acid. Citrates
are formed by replacing the acidic one, two, or all three of the carboxylic
hydrogens in citric acid by metals or organic radicals to produce an extensive
series of salts, esters, and mixed (solid) salts. Cirrates are used in food,
cosmetics, pharmaceutical and medicine industries as well as in plastic
industry; nutrient or food additives having functions of acidity regulator,
sequestering and stabilizing agent, antioxidants synergist, firming agent;
anticoagulant for stored whole blood and red cells and also for blood specimens
as citrates chelate metal ions and saline cathartics, effervescent medicines;
high boiling solvent, plasticizer and resin for food contact plastics. |
||